The Director-General of Police, Rajasthan, conducts an examination for the position of Rajasthan Police Constable once a year. The Physical Efficiency Test and the Physical Standard Test are conducted after the written examination for the Rajasthan Police.
Questions in the written exam for the recruitment of Rajasthan Police Constables will be drawn from topics such as Rajasthan’s history and culture, geography, economics, politics, general knowledge, current affairs, laws and regulations pertaining to crimes against women and children, reasoning, logic, and basic computer literacy, among others.
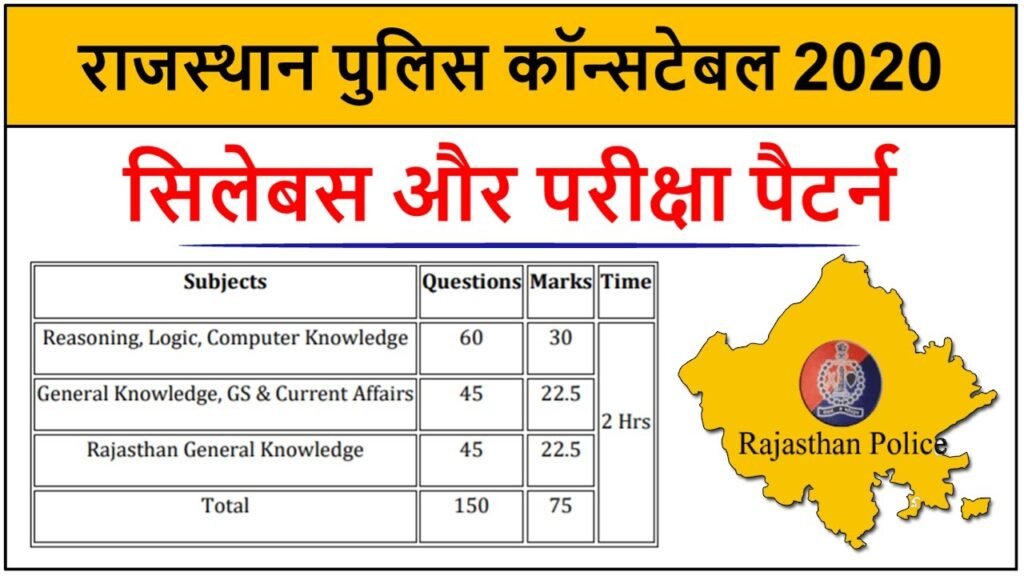
Exam Pattern for the Rajasthan Police
The written test for the Rajasthan Police Exam consists of a total of 150 questions, with the maximum possible score for the paper being 75 points.
The following table shows the distribution of marks and questions by topic, as indicated by the numbers in the table:
| Topics | Number of Questions | Marks |
| Reasoning Ability and General Computer | 60 | 30 |
| General Knowledge, Social Studies and Current Affairs | 35 | 17.5 |
| Knowledge of Laws and Regulations regarding Crimes Against Women and Children | 10 | 05 |
| History, Culture, Geography, Polity etc. of Rajasthan | 45 | 22.5 |
| Total | 150 | 75 |
Rajasthan Police Constable Syllabus is available online.
Each of the four components of the Rajasthan Police Constable examination is worth one point. Among the topics covered are Reasoning, Logical Abilities, and a basic understanding of computers; General Knowledge, Social Studies, and Current Events and Issues; Laws and Provisions related to Crimes Against Women and Children; and History, Geography, Culture, Economics, and Polity of Rajasthan. The exam is divided into four sections: Section – A (reasoning), Section – B (social studies), and Section – C (crimes against women and children).
The following is a summary of the fundamental syllabus for each of the sections:
| Sections | Subject | Topics |
| Section – A | Reasoning and Logic | Distance and Direction, Data Interpretation, Logical Reasoning, Analogy, Venn Diagrams, Coding-Decoding, Figure Completion, Simplification, Verbal and Non-verbal Reasoning, Arithmetic Reasoning, Clock, Calendar etc. |
| Basic Computer Literacy | Cyber Security, Internet, MS Office, Networking System, Hardware, Software, Viruses and Malware etc. | |
| Section – B | General Knowledge, Social Studies and Current Affairs | General history of India, Indian Polity and Governance, Famous Personalities, Science and Technology, Economics, Sports, Awards and Important Events |
| Section – C | Knowledge of Laws and Regulations regarding Crimes Against Women and Children | Awareness of crimes against women and children, legal provisions to prevent crimes and Safety Measures |
| Section – D | History and Culture of Rajasthan | Major Dynasties, Major Landmarks in the History of Rajasthan, Administration and Revenue System, Socio-cultural Issues, Freedom Movement, Political Awakening and Integration, Salient features of Architecture – Forts and Monuments, Arts, Paintings, and Handicrafts, Folk Dances, Literature and Art of Rajasthan, Local Dialects, Festivals, Fairs, Folk Music, Rajasthan Culture, Traditions and Heritage, Religious Movements of Rajasthan, Important Tourist Places and Leading Personalities of Rajasthan |
| Geography of Rajasthan | Natural Resources of Rajasthan, Climate, Natural Vegetation of Rajasthan, Forests, Diversity, Biodiversity, Agriculture, Major Irrigation Projects, Population, Minerals and Mines, and Major Industries and Potential for Industrial Development | |
| Rajasthan Polity | Governor, Chief Minister, State Assembly, High Court, Rajasthan Public Service Commission, District Administration, State Human Rights Commission, Lokayukta, State Election Commission, State Information Commission, State Information Commission, Public Policy, Legal Rights, Citizens’ Charter | |
| Rajasthan Economics | Macro-overview of the Economy, Major Agricultural, Industrial and Service Sector Issues, Growth, Development and Planning, Growth, Development and Planning, Infrastructure and Resources, Major Development Projects, Government Welfare Schemes, Minorities, Disabled Persons, Destitute, Women, Children, Old people, Famers and Labourers. |